Our website uses cookies, including third parties’ profiling cookies, to improve your user experience. You can learn more about how we use cookies and how to change your cookies settings in our Privacy Policy. By closing this message, clicking above or continuing to use this site, you consent to our use of cookies.
STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS OF ACTIVATED CARBON
Since creating the first activated carbon products from bituminous coal in the 1940s, Calgon Carbon has been a pioneer in developing advanced products, systems and services for air and water purification. We remain the innovators of new uses for activated carbon, offering an exceptional range of applications and reactivated carbon formulations.
Our product portfolio now encompasses more than 700 direct market applications, including several revolutionary industry developments such as:
- In the 1940s we offered coal-based activated carbon for use in military protection
- The “Pittsburgh Pulse Bed” the first activated carbon system for sugar decolorization in the 1950s
- The first use of granular activated carbon (GAC) for taste and odor removal from drinking water in the early 1960s
- The original Evaporative Loss Control Device (ELCD) application in the early 1970s
In this century, we launched FLUEPAC® powdered activated carbon for treatment of mercury in flue gas streams from coal-fired electric power plants.
And, for over 15 years, our much-requested FILTRASORB® activated carbon has been treating PFAS water contaminants that you hear about in the news. With over 45 installations for PFAS removal across the United States, our complete solution includes activated carbon, equipment, on-site installation and exchange services, reactivation and financing.
SO, WHAT IS ACTIVATED CARBON?
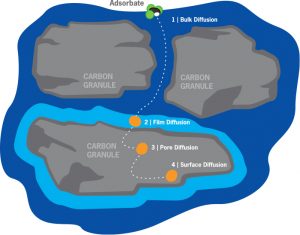
Activated Carbon is a porous material that removes organic compounds from liquids and gases by a process known as “adsorption.” In adsorption, organic molecules contained in a liquid or gas are attracted and bound to the surface of the pores of the activated carbon as the liquid or gas is passed through.
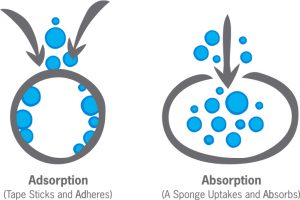
There’s a distinct difference between ADsorption and ABsorption:
The primary raw material used in the production of our activated carbons is bituminous coal that is crushed, sized and processed in low-temperature bakers followed by high-temperature activation furnaces.
The structure of our activated carbon is one of the reasons it’s considered the best in the market. It’s about what’s on the inside. Let’s take a closer look:

The structure of activated carbon is composed of graphitic plates. These plates are connected by carbon-carbon bonds, which create a porous structure and give an extensive internal surface area, which is where adsorption occurs. Adsorption is one type of Van der Waal’s force, which works on the molecular level to attract molecules to each other. With activated carbon, the surface of the carbon is attracted to the compound being adsorbed.
Intermolecular attractions in the smallest pore of the carbon particle result in adsorption forces that cause precipitation of adsorbates from solutions, and condensation of adsorbate gases.
Adsorbates actually undergo a type of phase change because they are so much lower in energy once they are adsorbed.
Spent activated carbon doesn’t swell like an ion exchange resin or sponge upon use. All of the work takes place inside the pores – deep inside the granules – where the water molecule at the surface is displaced by an adsorbate molecule.
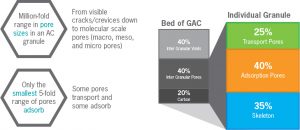
Activated carbon has a transport system with a variety of pore sizes:
- From very large transport pores to smaller transport pores
- With ability to handle high to low adsorbate movement rates
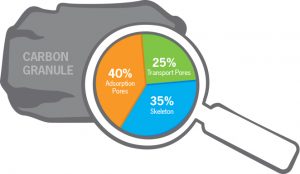
Magnifications of an activated carbon particle:
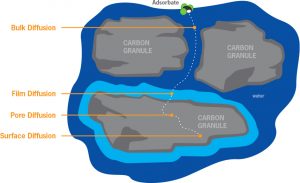
This final image shows the molecular structure of activated carbon that is saturated with adsorbate. The adsorbate needs to be close to a carbon plate to adsorb. Once the adsorbate is more than a few molecular diameters away from the carbon surface, adsorption does not occur.
STARTING MATERIALS OF ACTIVATED CARBON
While activated carbon can be made from any carbon-containing starting material, many have learned the hard way that the raw material dictates all product possibilities. Calgon Carbon sources the best raw materials in the world, and that is why our customers come back to us time and again. Starting with inferior raw materials, or using chemical treatments to upgrade those inferior raw materials, ends up costing customers more money in the end.

MANUFACTURING PROCESS OF COAL-BASED ACTIVATED CARBON
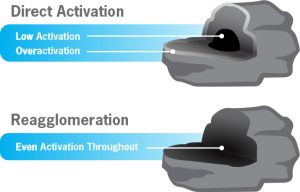
When choosing coal-based activated carbon, remember to ask this question:
IS IT REAGGLOMERATED?
Why? Because it’s better. And, just like demanding quality raw materials, you should demand a superior manufacturing process for your coal-based activated carbon, which is REAGGLOMERATION.
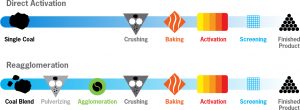
Manufacturing of Activated Carbon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag4fFJUmPmM
DIFFERENT TYPES OF ACTIVATED CARBON
GRANULAR ACTIVATED CARBON
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) is a specific preparation of activated carbon, or activated charcoal. It has been used as a purification agent since the early 19th century. Today, activated carbon in various forms, including granular, is used in a wide range of industrial, commercial, and home applications to remove contaminants.
The absorptive capacity of GAC makes it ideal for removing a variety of contaminants from water, air, liquids, and gases. GAC is an environmentally responsible product that can be reactivated through thermal oxidation and used multiple times for the same application.
As the world’s largest manufacturer of granular activated carbon, Calgon Carbon backs its products with comprehensive analytical support including feasibility studies and cost evaluations, together with complete system design, service and troubleshooting. Calgon Carbon brings unmatched expertise in developing GAC applications which means that whatever your GAC need, Calgon Carbon has a product engineered specifically to provide a better solution.
POWDERED ACTIVATED CARBON
Calgon Carbon Corporation manufactures many types of Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) products, each specifically engineered to provide a unique pore structure and adsorption properties.
The adsorptive capacity of Calgon Carbon’s PAC makes it ideal for removing various contaminants from water, air, liquid and gases. With efforts to be environmentally responsible, Calgon Carbon can reactivate spent Granular Activated Carbon through thermal oxidation to make “react” Powdered Activated Carbon.
Calgon Carbon brings more than 70 years of experience in producing powdered activated carbons specifically engineered to meet the demands of individual industrial applications. From residential and municipal water treatment to pharmaceutical product purification, and from food and beverage decolorization to energy storage, and much more — Calgon Carbon delivers a wide array of custom-engineered powdered activated carbons to better meet your needs.
PELLETIZED ACTIVATED CARBON
Pellets are activated carbon compressed into formed cylinders and have a wide variety of uses such as removing contaminants like volatile organic compounds and mercury from natural gas as well as controlling odor.
Pellets are specifically designed to provide a unique pore structure and adsorption properties. The adsorptive capacity of pelletized carbon makes it ideal for removing a variety of contaminants from air and gas streams. Pellets are also an environmentally responsible product that can be reactivated through thermal oxidation and used multiple times for the same application.
ACTIVATED CARBON CLOTH
Calgon Carbon is a pioneer in cutting-edge textile through its activated carbon cloth (ACC) used for medical, defense, and industrial applications.
Flexorb™ ACC is 100% activated carbon and is more effective at adsorption compared to other carbon loaded materials which have a lower activated carbon content.
Flexorb™ ACC has a microporous structure which results in rapid adsorption kinetics and the capability to adsorb to a higher level of purity. Flexorb™ ACC is also suitable for use in applications where there is a high humidity as its adsorption capacity is less adversely affected by moisture.
REACTIVATION SERVICES
We are an environmentally conscious company – sustainability has vital implications in what we do every single day. Recycling and reactivation are important parts of those initiatives. In fact, we have been recycling for years by reactivating spent carbon.
After an activated carbon adsorption capacity has been exhausted, it can be returned to Calgon Carbon for thermal reactivation. With high temperature reactivation followed by off-gas treatment, the adsorbed organic compounds are destroyed and reactivated carbon can be safely and cost-effectively recycled back to facilities for continued use.
A number of important steps occur in the reactivation process:
- Spent activated carbon is heated in furnaces devoid of oxygen using steam as a selective oxidant.
- Adsorbed organics are either volatilized from the activated carbon or pyrolysed to a carbon char.
- Volatilized organics are destroyed in the furnace’s afterburner.
- Acid gases are removed by means of a chemical scrubber.
- The high-temperature reaction with steam serves to restore the adsorptive capacity of the activated carbon.
Through reactivation, the spent granular activated carbon can be recycled for reuse, virtually eliminating the costs and long-term liability associated with disposal.
Activated Carbon Reactivation: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ufkh8Qm_SQE
